The intelligent information Request and Delivery Standard (iiRDS) is a technical standard for the delivery of digital information for use or technical documentation such as electronic operating instructions and user manuals. iiRDS can be used free of charge and is published under a Creative Commons license.
A group of experts at tekom started to develop iiRDS in 2016. In 2018, the iiRDS Consortium was established to maintain and further develop the standard. This year, the Consortium is prioritizing the request part of iiRDS as their major focus.
Benefits of iiRDS
iiRDS enables the manufacturer-independent delivery, exchange, and aggregation of information for use. This is particularly relevant in the context of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), where technical information from different manufacturers in plants and smart factories is combined.
iiRDS focuses solely on standardizing the exchange format and is not concerned with the way content is created and maintained. This focus on the delivery format for smart content enables iiRDS users to author the content using different programs, for example, content management systems.
The standard consists of a format that defines the file and folder structure of the package containing intelligent information as well as an ontology for enriching content with metadata.
Content enriched with iiRDS metadata supports functions for searching and filtering information and other content functionalities. This smart content can thus be found faster and more accurately in self-service portals, documentation portals, or apps.
A use case
Take the classic iiRDS use case of a service technician tasked with the maintenance or troubleshooting of a product: Here, iiRDS enables the display of the necessary information for the affected machine part that needs to be replaced and shows the relevant information – either directly on the product or via an associated app. The service technician doesn’t have to browse through manuals or PDF documents. Even if the service technician is used to classic information for use, he would have to either search in the PDF manually or the search results would depend on the exact term he has entered into the search bar.
Metadata is key for intelligent information. iiRDS provides the appropriate tools for modeling such use cases, thus offering the option to present information for use in an individual, user-oriented, and context-related way. This is especially beneficial for manufacturers of more complex products that integrate various components and the respective information from external suppliers, who use differing terminology. iiRDS standardizes metadata and provides a packaging format for archiving and exchanging technical communication.
Check out our best practice examples of iiRDS implementations.
Metadata model
iiRDS uses the Resource Description Framework Schema (RDFS) as the technical format for its metadata model. After registration, these RDF files can be downloaded from the iiRDS Consortium website for free.
| RDF Schema (RDFS) provides a data-modeling vocabulary for RDF data. RDFS is an extension of the basic RDF vocabulary and belongs to the family of semantic web standards maintained by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). A common vocabulary – or ontology – is needed to interpret statements formulated in RDF. RDF is not a metadata vocabulary, but a data model for statements about resources. It can be used to develop vocabularies such as iiRDS, which contains a vocabulary for technical communication. There are also other ontology description languages such as Web Ontology Language (OWL). For further information, visit the W3C website. |
iiRDS metadata can be assigned to text fragments, topics, or documents. The iiRDS metadata model is based on the PI classification by Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Ziegler (I4ICM) and defines the categories of metadata shown in Figure 1.
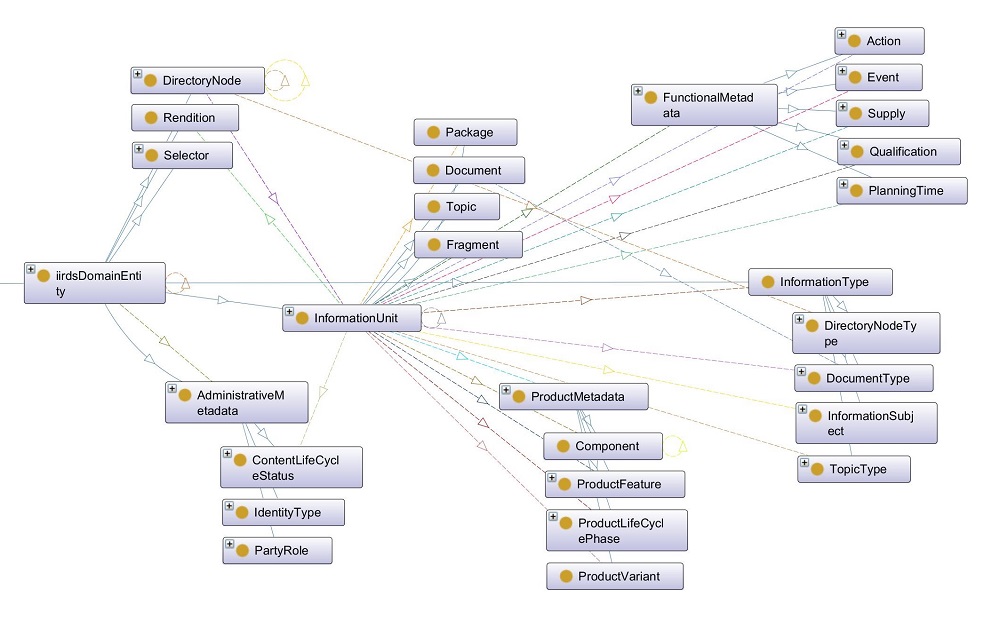
Figure 1: Excerpt of the iiRDS metadata in the Protégé tool
The metadata model can be extended by adding new subclasses or objects to existing iiRDS classes. iiRDS explicitly supports the extension of the metadata model and provides what are called “docking points” for linking external metadata, for example, product metadata or role and qualification definitions.
Delivery format
The iiRDS package is a ZIP file containing the content to be delivered and the associated metadata as RDF. iiRDS comes in two variants regarding the format of content:
- Unrestricted packages can contain any kind of format, for example, PDF, HTML, XML, MP4, SVG, or Office files.
- Restricted packages in the iiRDS/A format contain content only in predefined formats and are self-contained. The predefined formats are PDF/A, a restricted selection of media formats, and XHTML5 with element and attribute restrictions. iiRDS packages are self-contained when the content files only point to files within these packages. The restrictions of the iiRDS/A format aim to ensure that all iiRDS-capable applications process and present the content in similar ways without any additional implementation or customization effort.
Free iiRDS tools to get you started
iiRDS defines a standardized format for delivering smart content from an application that creates iiRDS packages from content (e.g., CMS, authoring or converter tools, iiRDS Open Toolkit) to an application that receives and processes iiRDS packages (e.g., content delivery portals or self-service portals).
To support the application, the iiRDS Consortium provides an Open Toolkit that can be used to enrich content with metadata. Users can upload the content in common formats such as PDF, Word, HTML, and XML files. It then generates a valid iiRDS package from content and metadata that the user can check and revise or add custom metadata. For more information, visit our iiBlog.
Since November 2022, the iiRDS Consortium also provides an iiRDS Validation Tool to validate iiRDS packages from other systems. These tools are available as a free web service on the iiRDS website.
Submodel development for interoperability
Members of the iiRDS Consortium are currently strongly engaged in the InterOpera Working Group “iiRDS Handover Documentation” to develop a submodel of the Asset Administration Shell (AAS). Assets in the AAS can communicate automatically. The AAS is the basis for interoperability and is the digital twin of, for example, a networked machine or plant. It provides a standardized semantic and technical mapping between the assets and the software systems involved. Simply put, different data formats are serialized and standardized so that they can be exchanged with stakeholders along the value chain.
In the industrial environment, most information for use, such as technical documentation or technical data, is still exchanged in paper form or digitally in document-based formats such as PDF. Much of this information contains no or inadequate metadata. This makes it difficult to find and efficiently use the information when it is needed. The iiRDS Handover Documentation submodel, based on the iiRDS standard, is intended to fill this information gap and to be established as a metadata model for intelligent information, which enables the efficient cross-manufacturer provision, exchange, and aggregation of information for use.
We also have a member in the InterOpera Working Group “Digital Standards Datasheet”. This submodel is intended to close the gap caused by proprietary management systems that are incompatible with each other, to provide information and meta information at the document level, so that partners in a value network can acquire, exchange, and apply standards interoperably. The aim is to enable, for example, the automated implementation of finding suitable standards for the certification of developed products.
Publications for both InterOpera projects via the Industrial Digital Twin Association (IDTA) are in the planning stage.
What’s on the roadmap for 2023?
Here’s a brief overview of the high-priority projects the iiRDS Consortium has planned this year:
The StandardsWorking Group has submitted a document outlining the basic iiRDS structure with the information flow model and metadata as a Publicly Available Specification (PAS) with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The document was revised in the IEC/TC 3/WG 28 and is now being voted on. Further steps towards international standardization of iiRDS are being discussed and undertaken in coordination with the Digital Data Chain Consortium (DDCC).
The Content-Tools-ValidationWorking Group is focusing on further developing and promoting the validation of iiRDS packages with the help of the iiRDS Validation Tool that is available on iirds.org. Other projects include the further development and maintenance of iiRDS Tools and considerations on DITA compatibility.
The DevelopmentWorking Group is currently busy finalizing the new release, including a terminology review and an external classification class. The iirds:ExternalClassification class will be added and can be used for standardized product classification such as ECLASS, CDD or bSDD (BIM), or alternative information classifications. There will be no downtime after the new release, as the working group will be involved with the Content-Tools-Validation Working Group in the request part tender and will consider requirements for smart standards.
The iiRDS Consortium is offering iiRDS Online Training from June 5-30, 2023 for all technical writers, information architects, and other experts in technical communication interested in getting a deeper understanding of iiRDS. Information and registration are available at www.iirds.org/iirds-training.
Getting involved
Here is how you can participate in iiRDS developments:
- Register on our website, iirds.org, and subscribe to our newsletter to receive relevant updates on new releases, events, webinars, training, and more.
- Upon registration, you can access the iiRDS materials and get started.
- Start an iiRDS pilot project accompanied by a Consortium member in the consultants pool. In 2022, the iiRDS Consortium agreed to support four pilot projects. A similar funding initiative is planned for 2023.
- Become a Consortium member. The iiRDS Consortium consists of industrial companies, system vendors, consultants, and service providers. If you are starting a pilot project or expanding your knowledge of iiRDS, please contact us. As a member of the Consortium, you get the chance to be part of the development of the standard. Join our working groups (Development, Content-Tools-Validation, Standards), online training, and the consultants pool. Discuss your experience with iiRDS experts and get first-hand insights into various projects on intelligent information.
iiRDS materials & webinars After registration, you can download the current iiRDS version and sample content, as well as the iiRDS Whitepaper. |

