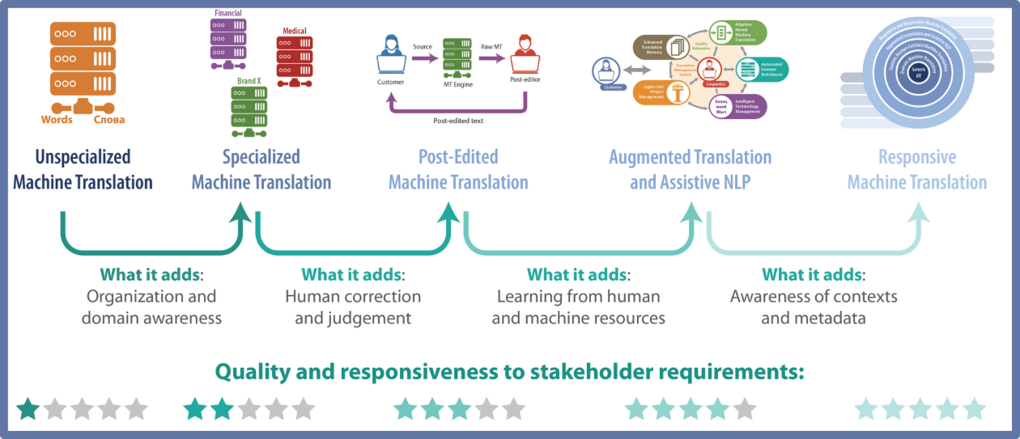
Since independent market research firm CSA Research first identified the advent of “Human-Enriched MT” in 2011 and “Augmented Translation” in 2016, MT has seen ever-accelerating adoption in the language industry. CSA Research’s latest report on MT, “Responsive Machine Translation,” predicts that current developments and trends in Artificial Intelligence development will result in machine translation that responsively adapts its output based on context, metadata, and usage scenarios.
“This advance will require substantial changes to core MT technology and how implementers interact with the technology,” comments Dr. Arle Lommel, senior analyst at CSA Research. “The magic behind the scenes involves increasingly sophisticated metadata and context that allow the emergence of ‘polymorphic MT engines’ that adapt dynamically to the content they translate in a way that current-generation MT systems cannot.”
Today's adoption of MT falls short of its potential
Through the course of seven decades of development, the technological underpinnings of machine translation have evolved and their applications have increased. In many aspects – most notably speed, volume, and cost – MT has far surpassed the capabilities of human translators. “However, some major MT developers even claim that their systems have achieved ‘human parity’ – that is, that their output quality is as good as, or better than, that of professional human translators. Nevertheless, users and suppliers alike still struggle with applying MT. They find that the output continues to fall short in many scenarios and remains far from meeting the standard expected for human translation,” comments Dr. Arle Lommel. “The focus of our latest MT research is on how the industry and technology will evolve to meet these shortcomings.”
The evolution of MT and its impact on the language services industry
This report explores how responsive MT will evolve and what it means for the language services industry, including:
- The four architectural foundations of responsive MT solutions
- The types of metadata that power polymorphic MT’s responsiveness
- Challenges in deploying metadata-driven MT and how to address them
- Developing “responsible MT” – the step beyond responsive MT – that can be trusted to meet a variety of ethical, legal, and regulatory requirements
- Recommendations for responsive MT for LSPs, buyers of language services, and technology vendors
Information sources
This guidance is based on CSA Research’s many interactions with machine translation developers and researchers, language service providers that deploy MT, and content creators who use the technology to facilitate their international work. In addition, the firm supplemented the findings with ongoing surveys of these constituencies about how they work with machine translation and other language technologies.
Related research
This report and its related research are available to CSA Research’s clients.

